Jamalpur community-based centre
Why community-based research?
Community-based research is a powerful model for engaging researchers and community members to solve pressing community problems or effect social change. Over few decades of research has shown that chronic noncommunicable diseases have their roots in unhealthy lifestyles or adverse physical and social environments. By impacting modifiable behaviours and risk factors, the burden of chronic disease problem can be reduced significantly. The community-based intervention or approach for the has a high degree of generalizability, cost-effectiveness due to the use of mass communication methods, ability to disseminate information through use of community networks, and potential for influencing environmental, regulatory and institutional policies that shape health.
 Community-based public health awareness campaign
Community-based public health awareness campaign Community-based public health awareness campaign
Community-based public health awareness campaign Classroom-based public health awareness campaign
Classroom-based public health awareness campaign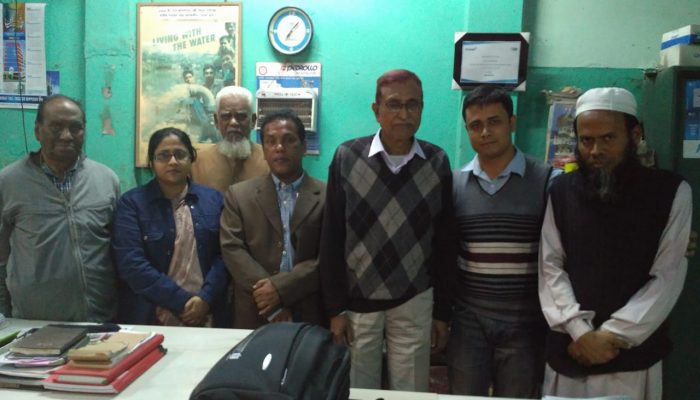 After a community-based public health awareness meeting
After a community-based public health awareness meeting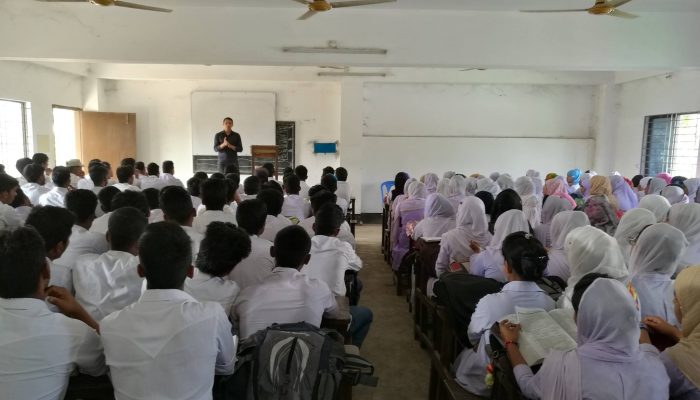 Classroom-based public health awareness campaign
Classroom-based public health awareness campaign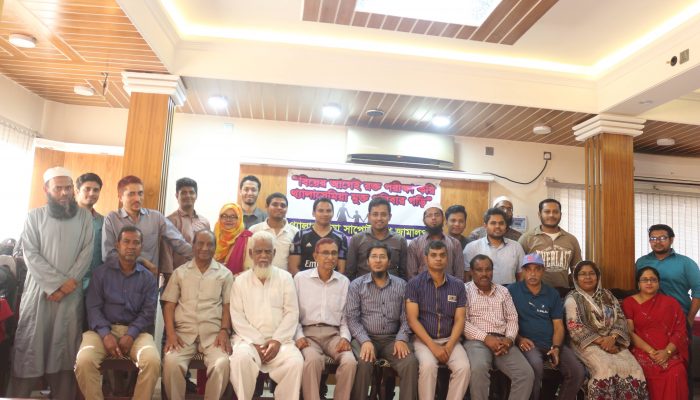 Community-based public health awareness committee
Community-based public health awareness committee
Why Jamalpur as a community-based research model in Bangladesh?
BRF is establishing Jamalpur district (one of the 64 administrative districts in Bangladesh) as a model for community-based chronic disease research. It has a population of 2.3 million (2011 census). Jamalpur with an area of 2031 square kilometer is located 140 kilometers (87 miles) northwest of the capital city, Dhaka. It consists of 7 sub-districts (upazilas), 6 municipalities, and 1532 villages. Nearly 95% of the population is Muslim, 4% Hindus and 1% others. This is one of the few districts in Bangladesh having indigenous people (for more info, see here).
In general, Bangladesh is homogeneous in terms of food habit, culture and socio-demographic factors apart from a few major cities. Our recent study has shown that Jamalpur is one of the thirty-five low-performing districts based on 79 maternal and child health indicators (Raheem et al 2019). We also found that this is closely related to one of the 33 districts in the context of demographic and socio-economic factors (Hossain & Hossain 2019). Therefore, community-based research findings obtained from Jamalpur could be generalizable to the major part of Bangladesh. Because of homogeneity, any successful intervention program could also be replicated in other regions of Bangladesh.
Our community-based resources
BRF is exploiting some underutilized resources including senior citizens, school/college teachers and religious leaders in the community to address public health problems such as thalassemia and childhood obesity in Jamalpur.
Ongoing community-based projects/activities
- Piloting of SUNRISE study (International surveillance study of 24-hour movement behaviours in the early years).
- College teacher based thalassemia prevention.
- Piloting of Blood for Thalassemia (BFT)- A community-based unique blood donation approach by utilizing an underutilized resource to solve blood scarcity in Bangladesh.
- Community-based support for thalassemia patients and their families.
